ACTIVATING THE INTERNET OF THINGS
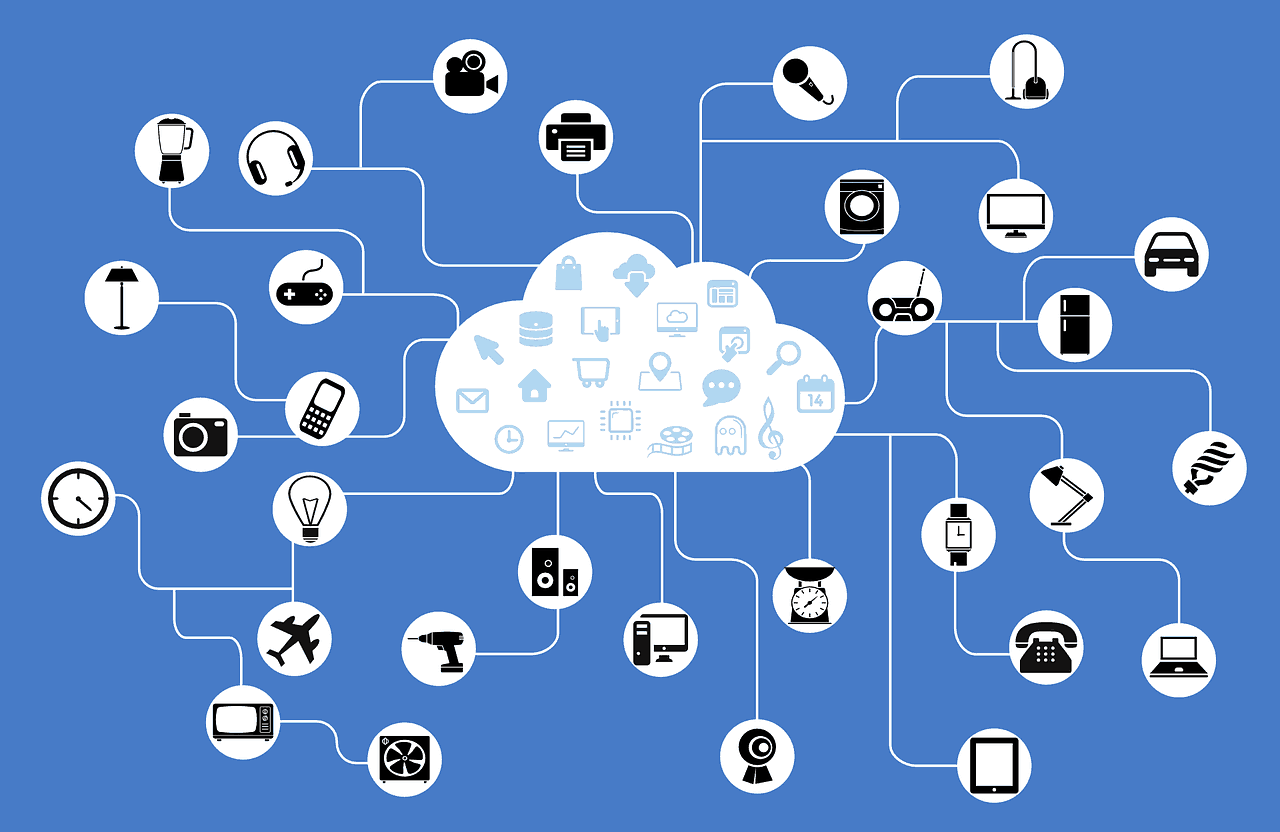
The Thing about IoT
The availability of broadband internet is now part of a social norm with 4.8 billion active internet users, representing 58% of the global population[1]. With the hike in smartphone usage reaching 3.2 billion in 2019, there is a simultaneous increase in more devices being built with Wi-Fi capabilities and smart sensors[2]. The global smartphone penetration rate is at 45.4%; whereas the smartphone penetration rate of Bahrain is 139%[3]. Taking all of this into consideration, such factors build the perfect landscape for the Internet of Things (IoT). The concept of IoT means that any device or component of a machine, practically anything that has an on and off switch, has the ability to connect to the internet or to each other and be part of IoT; whether it be at homes, buildings and cities.

“The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.”[4]
How does IoT work?
Sensors built into devices are connected to an IoT platform integrating data collected from different devices. Analytics is subsequently applied onto the collected data to share the relevant information within the network based on the nature of the situation and to address specific needs. The powerful platform can clearly identify and assess the type of information that is considered to be useful and what data can be safely ignored. Such information can later be used to detect patterns on users’ behaviors, suggest recommendations and spot problems prior to their occurrence. [5]

History of Internet of Things
Before the introduction of the term “IoT”, there was always a direct communication between machines with its initial form being the telegraph, the first landline developed in the 1830s and 1840s. Later in 1900, the introduction of the first radio voice transmission, considered to be a wireless telegraph, became a pivotal step in the development of IoT.
The whole concept of machine communication later came to be officially defined as IoT in 1999 through a Coca Cola vending machine located at a Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Programmers could connect to the machine through the internet with the purpose of checking drinks availability and temperature prior to making the trip for restocking or maintenance. By 2013, IoT evolved to what it is now with a network of connected automated technologies, wireless smart sensor networks, GPS, and control systems.[6]
Understanding the Conversation Between Devices
The usage of IoT opens up to a wide range of opportunities in everyday lives ranging from consumers to the management of businesses and to cities as well. The main reason for storing and sharing the data collected by devices through IoT is to improve efficiency and automate certain tasks that are either repetitive and/or time consuming. Therefore, IoT ultimately supports the overarching improvement of the quality of life. Applications of consumer, business, and city- based IoT devices include:
Consumers
There is a wide array of IoT devices that can either be installed at home or wearable devices such as cellphones, coffee makers, washing machines, lamps, and fitness devices. For instance, Google’s Nest thermostat serves as a self-learning Wi-Fi enabled thermostat which adjusts the home’s temperature based on certain factors linked to the consumer’s way of life and routine.
Businesses
IoT can be used to increase efficiency in business processes by automating complex business operations. The efficient process is associated with the wide connectivity of devices to the internet which results in businesses being smarter from real-time operational insights. Similarly, IoT also enhances asset utilization and runs preventive maintenance through the use of sensors. This results in the reduction of costs due to the improved asset utilization and operation efficiencies. Businesses can also integrate IoT with sensors and video cameras to monitor the workplace; thus, improving safety and security.
Cities
Cities can make use of IoT technologies to cope with the effect of population and economic growth. Aggregated data collected by IoT devices is mostly used to improve the living experience of people in terms of using public utilities as well as having the data readily available for agencies that provide such services to the community. Cities typically use IoT technology to mainly reduce traffic congestion, address environmental problems and safety issues. For instance, data collected through IoT has been used to automate street and traffic light, optimize trash pickup and augment surveillance and crime prevention.
Connectivity with IoT
Financial Services
The market size of IoT in the financial services industry is expected to grow to exceed $2 billion by 2023.[7] Some of the use cases are in wealth management personalization, enhanced payment security and transaction automation. The technology is mainly used for the improvement in the accuracy and the time taken to gather information, create seamless payment methods through smart card technology or wearable payment systems, as well as build a controlled trading environment with smart sensors and connected applications.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is at the forefront of IoT implementation through hardware and software systems. The utilization of IoT in healthcare organizations is mainly to improve services and enhance customer experience whether it be at the bedsides, waiting rooms, emergency rooms, or business offices. Various wearable hardware devices are available for the use of consumers to monitor their health such as fitness gadgets and bands. Certain devices also help medical officials track staff members and patients, monitor equipment for maintenance and ensure the timely dispensation of medication.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry has shown the greatest transition from IoT where selected business areas are either supported by IoT or have already deployed the technology across the organization. Manufacturers currently utilize IoT devices and sensors for operations from inventory and warehouse management, assembly operations on the ground, and tracking the movement of goods. Additionally, manufacturers have taken advantage of IoT for tracking energy efficiency where data collected from IoT devices is useful for providing visibility on machinery operations and receiving insight for waste management and results of behavioral changes.
Transportation
IoT can be applied to both public and private transportation in order to further increase mobility and accessibility as well as strengthen passenger service. A prime and popular example is self-driving vehicles that require a vast quantity of data collection from the connectivity of IoT in order to update its algorithms. Similarly, railroad tracks take the advantage of cameras and sensors to monitor wheel assemblies or track any abnormalities with freight cars.
Agriculture
The agriculture sector makes use of IoT devices and equipment to monitor the agricultural landscape such as checking soil and air quality by the installation of smart water control pumps and chemical level monitors. The technology in the sector allows real-time changes in the agricultural process thus increasing production.
How can IoT help your business stay connected?
As an individual, you can learn about how your business can benefit from the communication between IoT devices through the BetaBlocks Academy. You will learn about IoT, architectural overview, building an IoT device, latency and security.
BetaBlocks Academy
The FinTech Consortium Institute, in collaboration with BetaBlocks Academy has launched an online program that can help you sift through the chaos and be the building block of getting into specialized courses. The program provides a comprehensive overview of five key emerging technologies at the center of the digital revolution and complete a learning journey of specializations in Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things, Cybersecurity, and the Cloud. These courses form the building blocks required for a complete learning journey, leading to specialized courses in emerging technology applications for industries such as finance, supply chain and healthcare.
The courses are thorough, but not overly technical. They are designed to offer the most benefit to business professionals who want to understand the basics of how these technologies work, the benefits they offer, and how they can be applied to industries in transformative ways.
Successful application of emerging technologies can solve business problems and increase efficiency. Naturally, that creates persistent demand for qualified talent to lead these transformations. Stay ahead of the game by getting the training you need to succeed.
Do you wish to expand your career but don’t know where to start? Give your skillset a boost with the most relevant knowledge, including practical applications in your field. Bring yourself closer to your dream career.
Our courses provide clear structure, while letting you set the pace. Start something today that your future self will thank you for.
To learn more about the BetaBlocks Academy and the knowledge you could access through this platform, check out https://www.bahrainfintechbay.com/.
Credits: Bahrain FinTech Bay
Notes
[1] Statista. (n.d.). Global digital population 2020. Retrieved from https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/
[2] Find out How Many People Have Smartphones in 2020. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.oberlo.com/statistics/how-many-people-have-smartphones
[3] 2.34 million broadband subscribers in Bahrain | THE DAILY TRIBUNE | KINGDOM OF BAHRAIN. (2019, September 18). Retrieved from https://www.newsofbahrain.com/business/57033.html
[4] McClelland, C. (2020, January 9). What Is IoT? – A Simple Explanation of the Internet of Things. Retrieved from https://www.iotforall.com/what-is-iot-simple-explanation/
[5]Clark, J. (2016, November 17). What is the Internet of Things, and how does it work? Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/blogs/internet-of-things/what-is-the-iot/
[6] Foote, K. D. (2016, August 6). A Brief History of the Internet of Things. Retrieved from https://www.dataversity.net/brief-history-internet-things/
[7]How IoT is Changing Financial Services and Banking. (2019, June 6). Retrieved from https://www.digiteum.com/internet-of-things-banking-finances













